Information on cleaning, disinfecting and sterilizing medical instruments and devices
Medical instruments and devices and their daily use play an important rolewithin every veterinary practice. Correct disinfection also plays an important role in minimizing the risk of infection and protecting both users and patients over the long term.
This chapter focuses on the reprocessing of surgical instruments.
General Preparation
General preparation
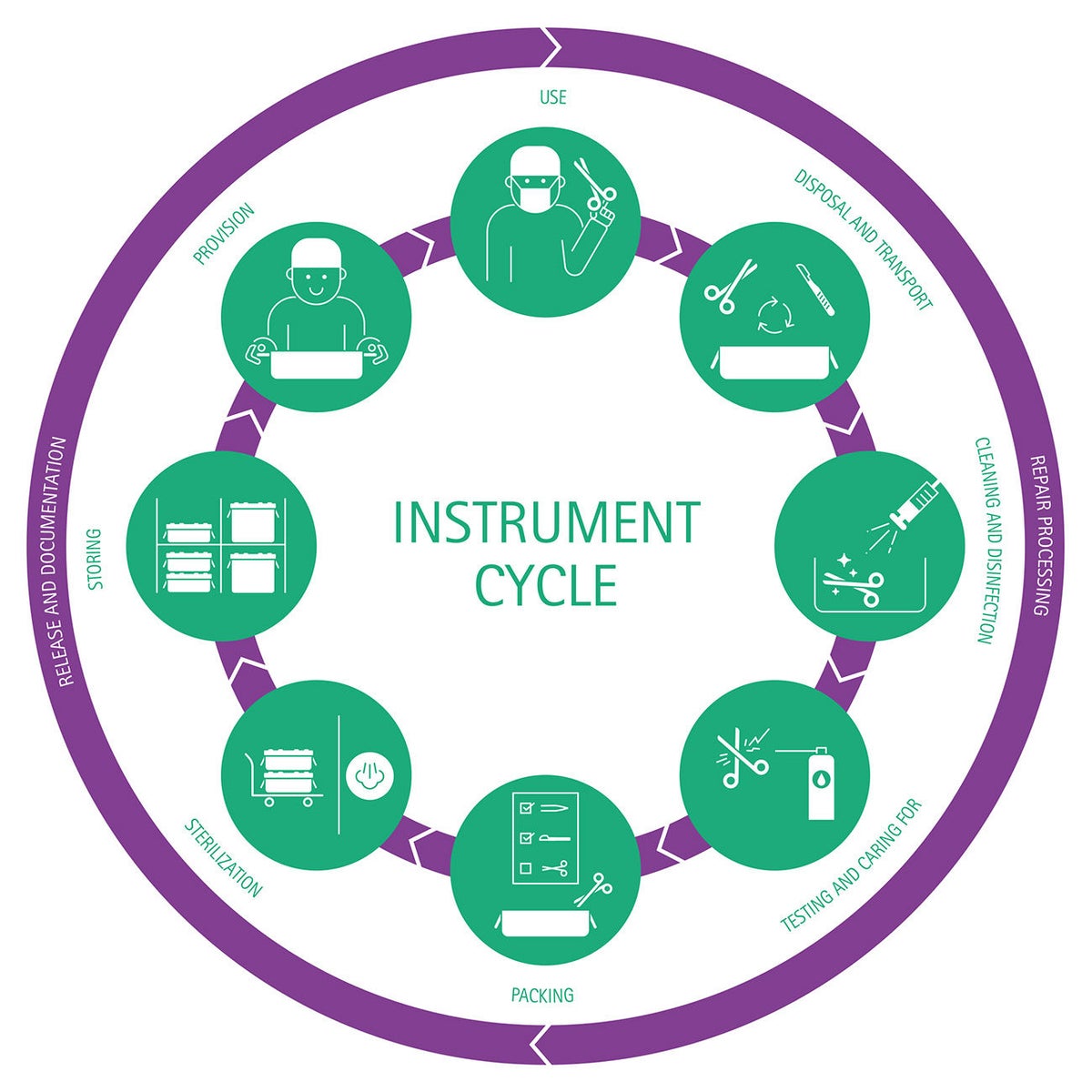
Reprocessing steps
It is recommended to observe the following individual steps for the proper reprocessing of medical instruments and devices. This ensures consistent quality and at the same time the protection of users and patients.
- Pre-treat, collect, pre-clean and disassemble if necessary
- Transport to the reprocessing location
- Clean/disinfect, rinse and dry
- Check for cleanliness and integrity
- Care and repair
- Functional test
- Labeling if necessary
- Package and sterilizen
The reprocessing process ends with the documented release of the medical device for use.
Classification of instruments and devices (hereinafter referred to as medical devices)
Before reprocessing, a risk assessment and classification of every given medical device must be carried out. It must be specified in writing whether, how often and with which procedures a given device is to be prepared.
Categories for which different reprocessing steps are recommended are distinguished and classified as follows:
- Non-critical: medical devices that only come into contact with intact skin e.g., stethoscope, ultrasound head.
- Semicritical: A and B are medical devices that come into contact with mucosae or diseased skin e.g., speculum.
- Critical: A, B and C are medical devices for the use of blood, blood products and other sterile medicinal products as well as medical devices that penetrate the skin or mucosa and come into contact with blood, internal tissues, or organs, including wounds e.g., dissecting scissors.
Poster
Reference
Our tip
AKI Brochure
A comprehensive reference work for instrument reprocessing in the veterinary sector is available from the Instruments Reprocessing Working Group (AKI) website.
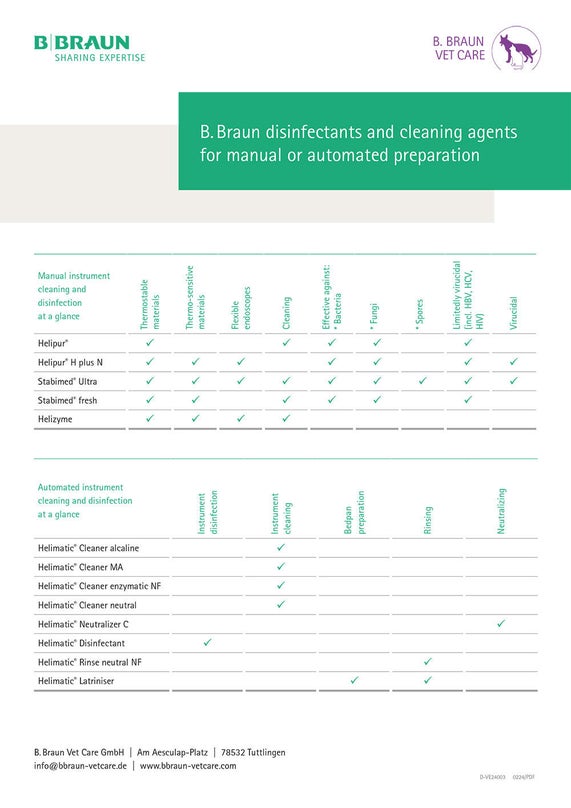
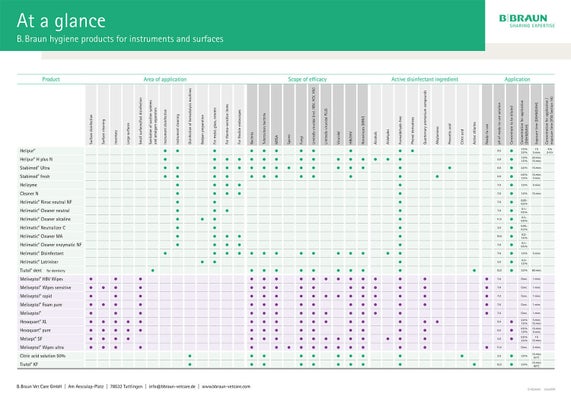
Choice of cleaning agents and reprocessing
When reprocessing medical devices, the manufacturer of the medical devices is obliged to provide information on suitable reprocessing procedures. Formulations such as “Reprocessing with alkaline agents containing detergent additives” are often used to avoid mentioning product names directly. The cleaning and disinfecting agents of B. Braun SE that correspond to these descriptions can be taken from the following table.
Table
B. Braun disinfectants and cleaning agents for manual or automated preparation
Treatment of brand-new instruments
Clean brand-new instruments prior to the first sterilization or use. Protective caps and protective films must be removed completely, e.g., chisels, raspatories or microsurgical instruments.
Cleaning-disinfection-sterilization of power systems and handpieces
AESCULAP® power systems and handpieces are low-maintenance and renowned for their reliability. Premature wear and malfunctions can be prevented by observing the general care instructions and the special care instructions in the respective instructions about the greasing of the handpieces. If repairs or functional checks are still necessary, please contact our Customer Management colleagues or your responsible Sales Partners.
Reprocessing Steps
Reprocessing steps
After use
- Reprocess contaminated instruments as quickly as possible.
- For mechanical cleansing, place the instrument into wire baskets suitable for cleaning (avoid any rinsing blind spots).
- Disassemble any instruments that can be taken apart.
- Dispose of any used equipment preferably in a dry condition.
- For wet disposal, use cleaning-active disinfectants. Prior to mechanical cleaning and disinfection, rinse the instrument thoroughly with clear running water.
If necessary, carry out ultrasound treatment according to the instructions of the device manufacturer:
- As an effective mechanical aid.
- For pre-treatment of instruments with dried-on dirt prior to mechanical cleaning.
- Microinstruments and instruments with fine working tips should not be ultrasonically cleaned, but rather cleaned manually or mechanically. For mechanical cleaning, store micro instruments in suitable storage aids.
- Clean manually or mechanically. Follow the manufacturer's instructions.
Practical tips
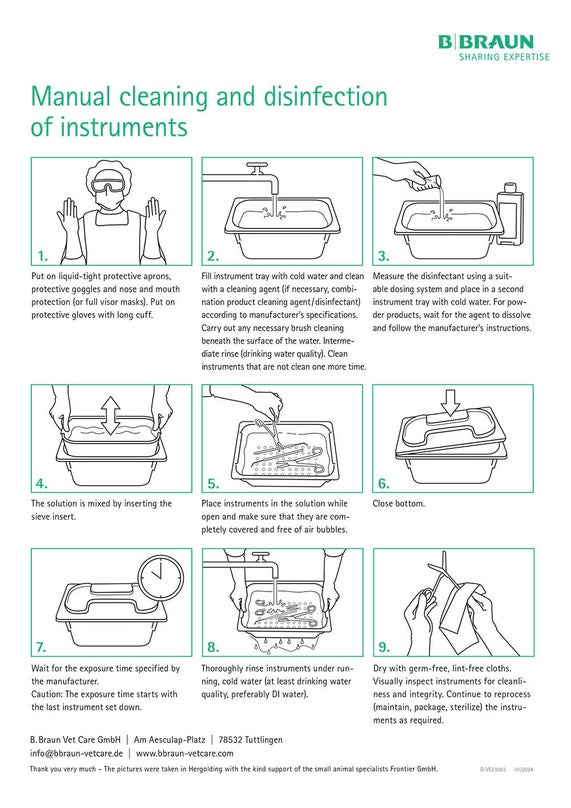
Manual Cleaning / Disinfection
Manual cleaning / disinfection
- Place instruments in a suitable active cleaning disinfectant in such a way that all surfaces, cavities, lumina, and openings are covered. Follow the disinfectant manufacturer’s instructions.
- Remove any dirt with a soft plastic brush. Do not use abrasive cleaning agents or metal brushes.
- Clean lumina and channels with soft round plastic brushes. The diameters of the lumen and the brush must match.
- Cary out interim rinsing.
- Place the instrument in a suitable disinfectant again.
- Always rinse thoroughly and intensively with clear running water after chemical disinfection. Follow the disinfectant manufacturer’s instructions.
- Carry out a final rinse with distilled or fully desalinated water.
- Dry the instrument with an absorbent, soft and lint-free cloth.
- Dry lumina and channels with compressed air.
Products for thermostable materials
Products for thermolabile materials
Step-by-step guide
Machine Cleaning / Disinfection
Machine cleaning / disinfection
- When selecting a program, take into account the material (e.g., stainless instrument steel, aluminum) of the instrument to be cleaned. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Carry out a final rinse with fully demineralized water.
- Maintain a sufficient drying phase.
- Remove the instrument from the machine immediately after completing the program.
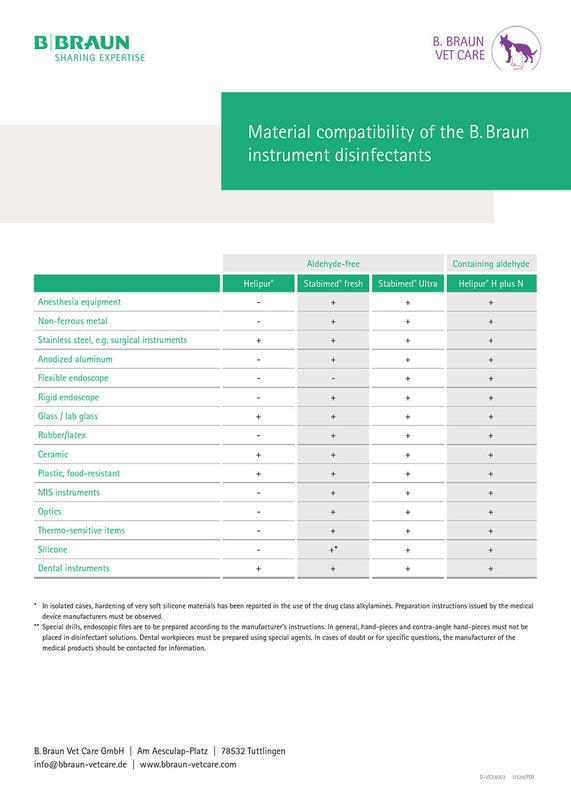
Material Compatibility
Material compatibility
Medical devices must always be reprocessed in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions. This is the only way to ensure that instruments are reprocessed with the appropriate active ingredients while at the same time ensuring that the full value of the work material is retained.
The following overview can be used for guidance on the material compatibility of B. Braun instrument disinfectants.
Table
Aesculap Online Service
Aesculap offers rapid and comprehensive information on the correct ways of reprocessing its instruments on its website: Electronic Instructions for Use (eIFU).
As soon as you have accepted the terms of use, the respective instructions for reprocessing can be called up after entering the article number of the instrument.
A safe combination: Aesculap and B. Braun
All B. Braun instrument disinfectants have been tested for material compatibility with Aesculap instruments.
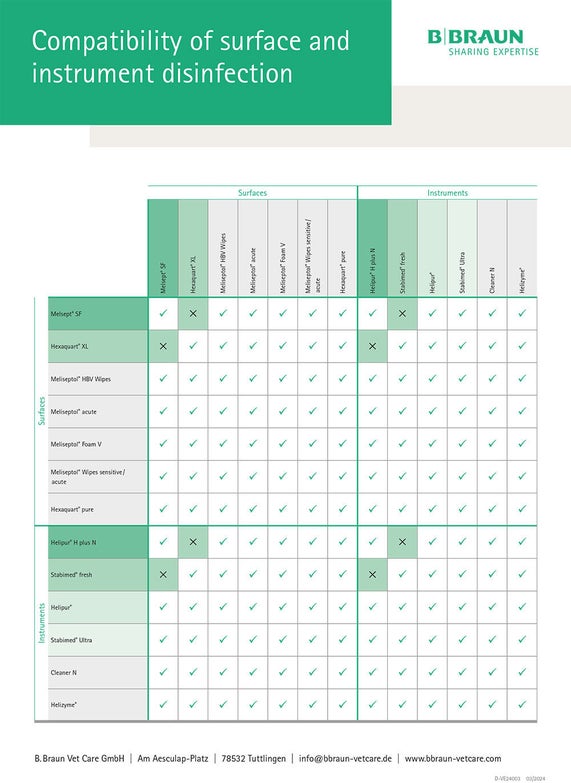
Biocompatibility
When using instrument and surface disinfectants in daily practice, the selection of disinfectant agents is of particular importance. In addition to the differing suitability for certain materials and the differing spectra of action, it must be ensured that the active ingredients of the products used are compatible with each other in order to prevent undesirable reactions.
Table
Table
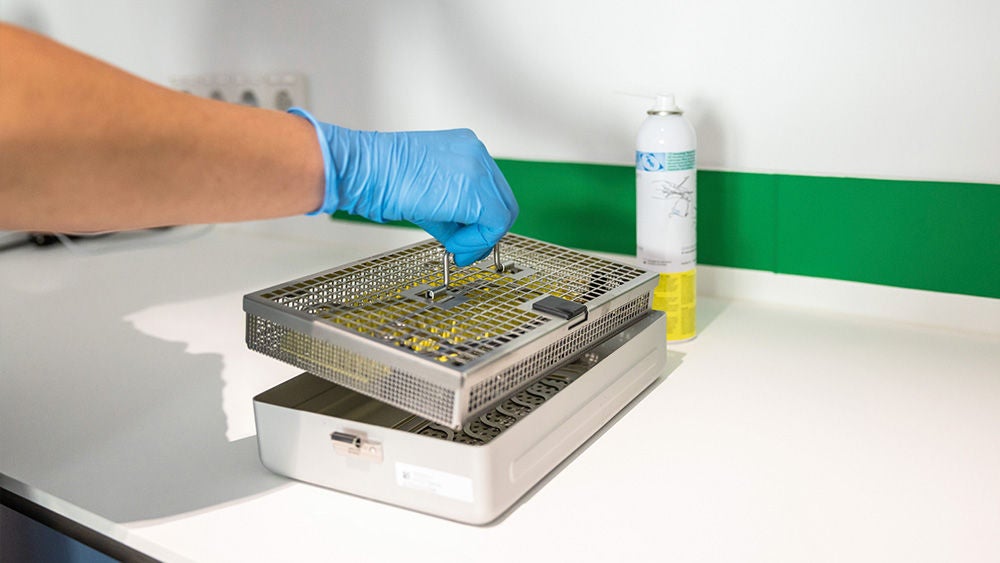
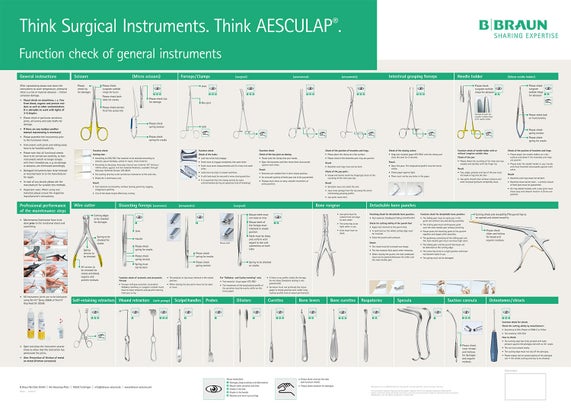
Care / Checking / Packing
Care / checking / packing
Maintenance / testing
- Allow the instrument to cool down to room temperature.
- Lightly lubricate moving parts (e.g., joints and latches) with sterilizable, steam-permeable maintenance oil (e.g., Sterilit® oil spray JG 600 or JG 598 care oil, physiologically safe according to DAB and Section 31 of the German Food Law (LMBG)).
- After each cleaning and disinfection cycle, inspect the instrument for cleanliness, function, damage and rust, as well as bent, broken, cracked, worn or fractured components.
- Set aside and replace any damaged and/or defective instruments.
Packing
- Store instruments with fine working tips and/or microsurgical instruments in suitable storage containers.
- Lock the instrument only up to the first notch.
Sterilization
Sterilization
Steam sterilization must be carried out using a validated steam sterilization process (e.g., sterilizer in accordance with EN 285 and validated in accordance with EN 554). If the fractionated vacuum procedure is used, sterilization must be carried out using the 134° C/2 bar program with a minimum holding time of 5 minutes.
Reference
Our tip

AKI Brochure
A comprehensive reference work for instrument reprocessing in the veterinary sector is available from the Instruments Reprocessing Working Group (AKI) website.